Causes and mechanisms of development
- Congenital disorders of spinal development or connective tissue defects;
- Injury or frequent overload, heavy physical work;
- Poor posture, flat feet, wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- Maintaining uncomfortable postures and sedentary lifestyles for long periods of time;
- Obesity, malnutrition, overweight;
- Exposure to chemicals, such as having bad habits or taking certain medications;
- often under stress;
- The natural process that occurs as the body ages;
- Continuous vibration has an impact on the spine.
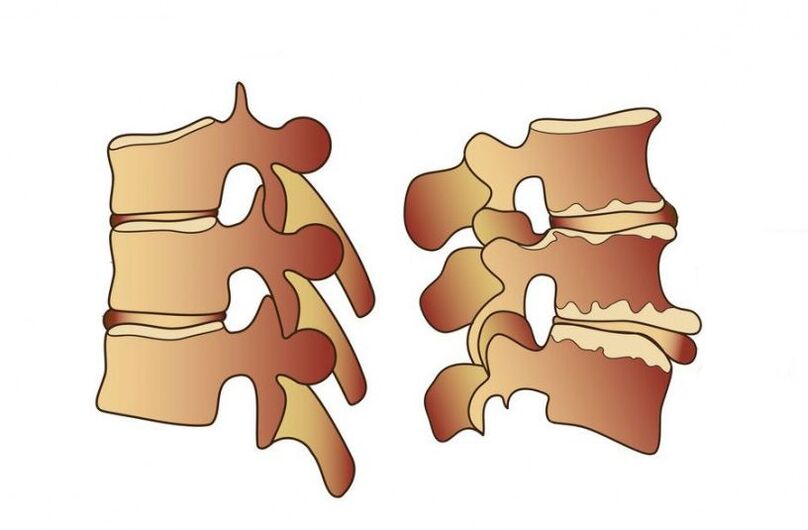
symptom
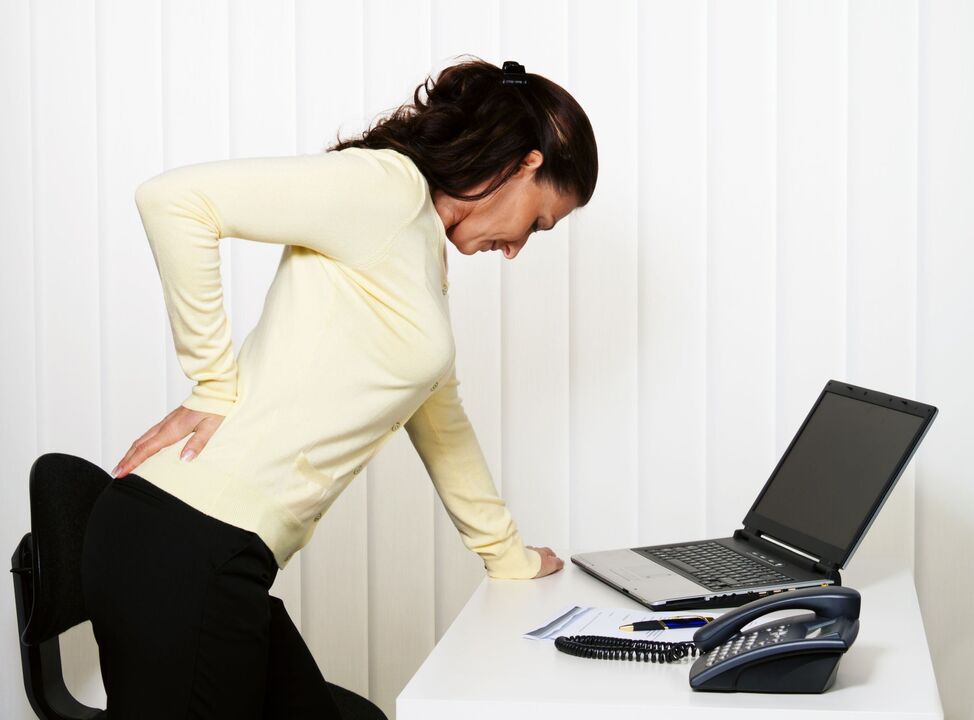

Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
- numbness in lower limbs;
- Impaired skin sensitivity and possible paresis;
- Pain is felt in the pelvic organs, their functions are disturbed;
- The patient is unable to turn or bend over and has pain even while sitting.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
- Headaches that are not relieved by conventional analgesics;
- Dizziness when turning the head;
- Pain may be felt in shoulders, back of head, and arms;
- Decreased vision, with spots or stains visible in front of the eyes;
- Have hearing loss and tinnitus;
- Tongue and fingers become numb;
- Impaired coordination of movements.
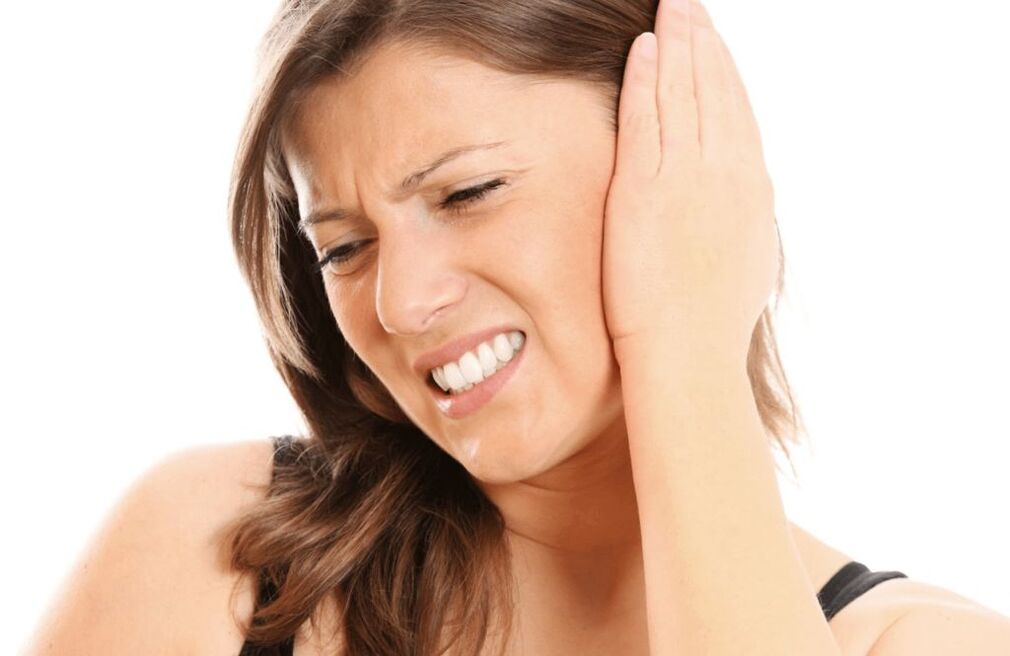

Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
diagnosis
radiography
myelography